World 🢖 Africa 🢖 Mauritania
Impact craters 🢔 Geological wonders 🢔 Categories of wonders
Wonder
Tenoumer crater

 In short
In short
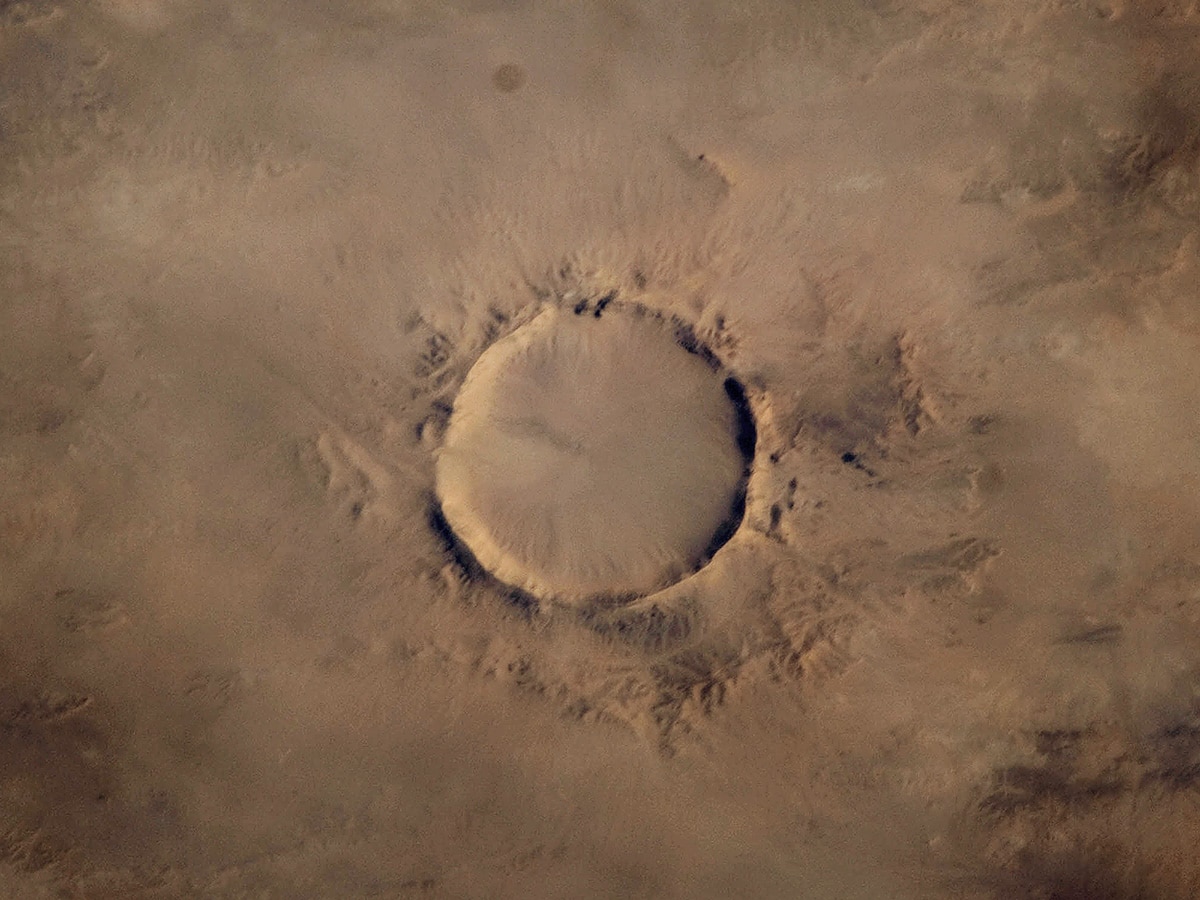
One of the best preserved impact craters on Earth is Tenoumer crater in Mauritania. This 1.9 km wide and up to 110 m deep crater is almost perfectly circular and was created by meteorite in Pleistocene, approximately 21,400 ± 9,700 years ago
 42.3%
42.3%
GPS coordinates
Location, address
Diameter
Depth
Age
Map of the site
If you see this after your page is loaded completely, leafletJS files are missing.
 In detail
In detail
Meteorite or volcano?
Guelb Tenoumer with its perfectly circular form is well known to local people and also Europeans since older times. Already in the 1950s scientists started a discussion whether this crater was formed by a volcano or meteorite.
At first the scattered rocks similar to basalt and rhyodacite around the crater created an impression the this is an ancient volcano. Convincing proof in the favour of meteorite impact was discovered in 1970 when key characteristics of outer impact – planar deformation features – were found in the supposed "lava". Since then it is widely accepted that the Tenoumer crater has been created by meteorite impact.

Three meteorites at once or three different events?
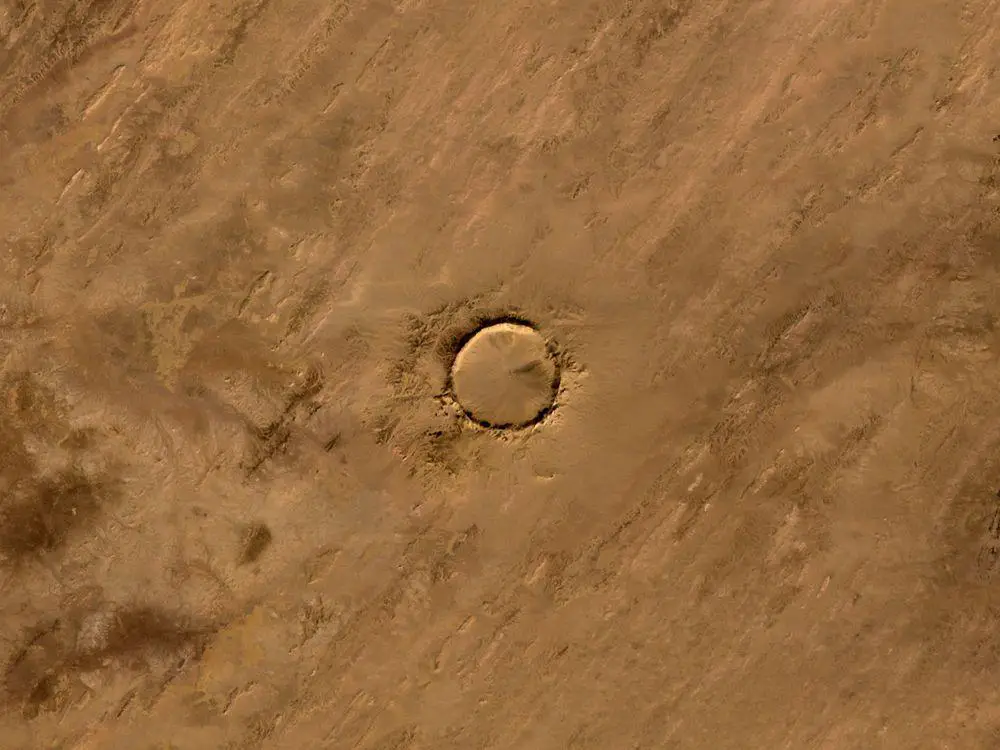
Mauritania has several impressive craters, which are aligned approximately on one line – Aouelloul crater, Tenoumer crater and Temimichât-Ghallaman crater. It is tempting to assume that all three craters were created by one single, catastrophic shower of meteorites.
Further investigations though show that this is not true. Aouelloul crater is old – approximately 3.1 million years. Age of Temimichât-Ghallaman crater is not known, there are discussions still, whether this is impact crater. Tenoumer crater is comparatively new – approximately 21,400 years.
Geology
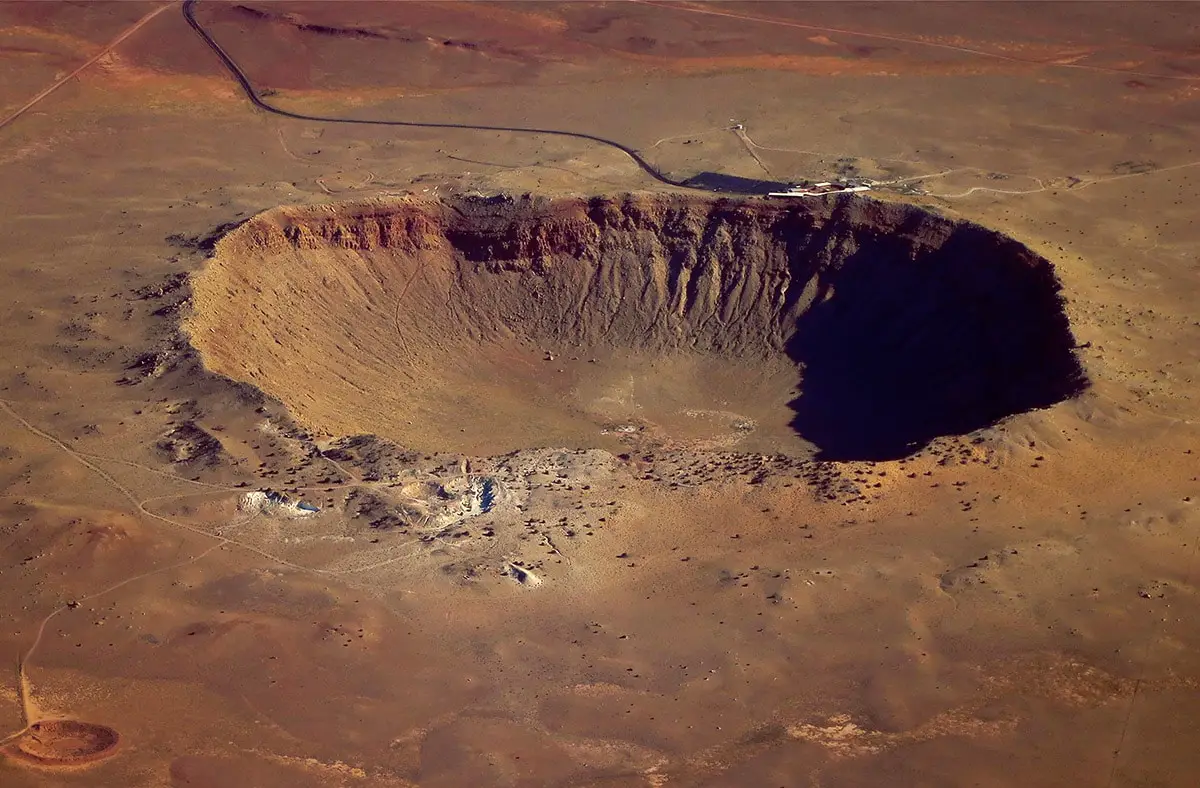
Diameter of this amazingly circular crater is 1.9 km. Rims of the crater rise some 110 m above the bottom of crater. Research though shows, that this crater is filled with approximately 200 – 300 m thick layer of unconsolidated sediments. Thus Tenoumer crater is very impressive structure, even larger than the famous Barringer crater in Arizona, United States.
Meteorite hit very hard rock – this area is formed from approximately 3.5 billion years old Precambrian gneisses and granites (Reguibat shield), which are covered with thin crust of weathered rock. It is hard to comprehend, how powerful should be an explosion which blasts and melts thousands of tons of such hard stone.
Inner slopes of crater are very steep. Around the crater, mainly to the east, northwest and southwest, are scattered blasted pieces of melted rocks. These pieces are up to 20 m long and contain small, fractured glass inclusions, also other deformations of rock grains have been observed.
No pieces of meteorite, even no traces of it in the surrounding rocks have been found thus far.
References
- Storzer D., Sélo M., Latouche L., and Fabre J., The Age of Tenoumer Crater, Mauritania, Revisited. Lunar and Planetary Science XXXIV (2003). Accessed on December 26, 2012.
Tenoumer crater is included in the following articles:
 Linked articles
Linked articles

Impact craters
There are many pieces of solid matter flying around in space. And VERY frequently they fall on the surface of the Earth. There are estimates that every year on Earth fall 18,000 – 84,000 meteorites larger than 10 grams: e.g. one meteorite every 6 – 30 minutes.
This category includes outstanding impact craters – detectable scars on the surface of Earth left by a body coming from outer space. The category includes also meteorites – natural objects from outer space.

Wonders of Mauritania
Almost all of Mauritania today is desert – somewhere desolate, somewhere – with some plants, lakes, and animals.
In earlier times nature here was less harsh, and great cultures developed. People from those times have left countless cliff paintings and etchings, megaliths, and abandoned towns.
Nature of Mauritania also provides surprises – giant, smooth, and very dark granite monoliths that rise hundreds of meters above the desert, and even a wealth of life – millions of birds at the ocean, or unusual dwarf crocodiles in the desert plateau of Tagant.

Wonders of Africa
Africa has many outstanding wonders and some of the most surprising ones are the heritage of Egyptian civilization, the vernacular architecture of the Sahel region, tropical ecosystems, and others.
 Recommended books
Recommended books
Africa’s Top Geological Sites
Africa is home to more than the Cradle of Humankind. It was the core of the ancient supercontinent Pangaea and comprises some of the oldest and most extraordinary geology on planet Earth. This detailed and colorful book features 44 of the continent’s most spectacular and interesting ‘geosites’, from Table Mountain in the south to the eroded necks and plugs of the Hoggar region in Algeria.
Travels in Mauritania
When Peter Hudson set off for Mauritania, he knew it only as a big blank space on a map of Africa. Traveling from the capital, Nouakchott, hardly more than a desert encampment, he found among the oases and ancient caravan towns a people in harmony with their harsh surroundings.